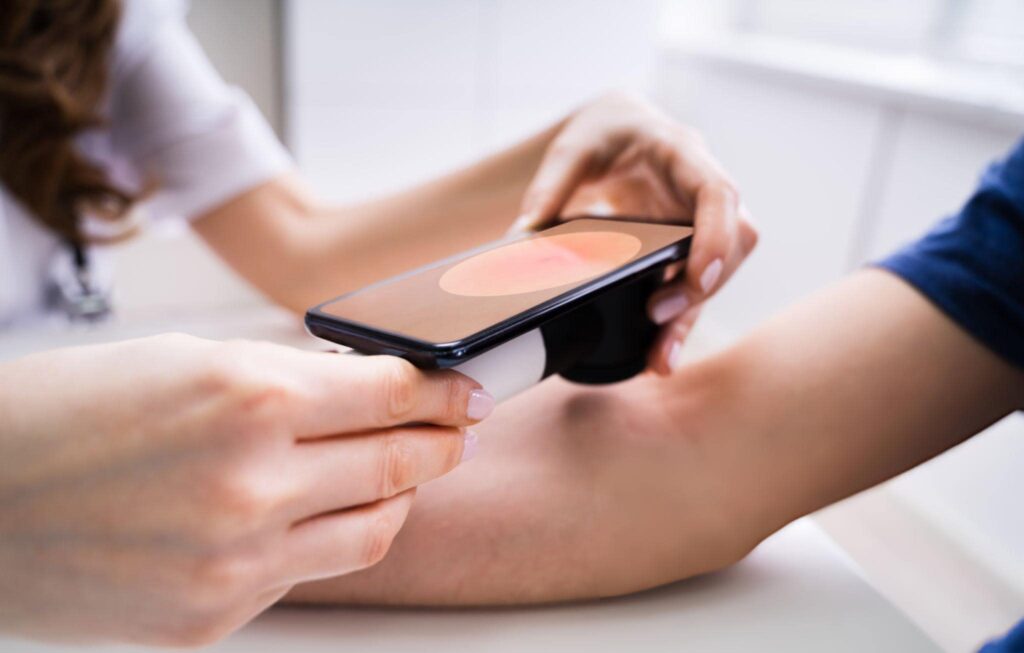
Skin cancer is a major health concern in Australia. With high exposure to UV radiation, the risk increases significantly. Many myths surround skin cancer, leading to misinformation and delayed diagnosis. Knowing the truth about skin cancer helps with early detection and prevention.
What Is Skin Cancer?
Skin cancer occurs when skin cells grow abnormally due to damage, primarily caused by UV radiation from the sun. There are three main types:
- Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC): The most common type, often appearing as a painless, pearly bump.
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC): May appear as a rough, scaly patch or open sore that does not heal.
- Melanoma: The most dangerous form, developing in pigment-producing cells. It can spread rapidly if untreated.
Early skin cancer checks improve survival rates. Misconceptions about skin cancer prevent many from seeking timely medical attention. Here are the most common myths and the facts behind them.
Myth 1: Only Fair-Skinned People Get Skin Cancer
Fact: Skin Cancer Can Affect Everyone
People with darker skin have a lower risk but are still vulnerable to skin cancer. Skin cancer symptoms may be harder to detect on darker skin, leading to delayed diagnosis. Regardless of skin tone, regular skin checks are essential.
Myth 2: Skin Cancer Only Develops on Sun-Exposed Areas
Fact: It Can Appear Anywhere
While sun exposure increases risk, skin cancer can develop in areas with little or no sun exposure, including:
- Under fingernails and toenails.
- On the palms and soles.
- Inside the mouth or on the genitals.
A full-body skin cancer check is crucial for early detection.
Myth 3: You Don’t Need Sunscreen on Cloudy Days
Fact: UV Rays Penetrate Clouds
Even on cloudy days, up to 80% of UV radiation reaches the earth’s surface. Applying sunscreen daily helps protect your skin. Sunscreen should be at least SPF 30 and broad spectrum for full coverage.
Myth 4: Skin Cancer Is Always Visible
Fact: Some Types Are Hard to Detect
Some melanomas do not follow the typical appearance of a changing mole. Certain types, like nodular melanoma, can be colorless or appear as a raised, firm lump. Regular skin cancer checks help detect these early.
Myth 5: Skin Cancer Is Not Dangerous
Fact: It Can Be Life-Threatening
If untreated, skin cancer can spread to other organs. Melanoma is especially aggressive, but early detection improves survival rates. Regular skin cancer screenings are essential for early diagnosis.
Myth 6: Tanning Beds Are Safer Than Sun Exposure
Fact: Tanning Beds Increase Skin Cancer Risk
Tanning beds emit concentrated UV radiation, increasing the risk of melanoma by 75% if used before age 35. There is no such thing as a safe tan from a tanning bed.
Myth 7: No Symptoms Mean No Skin Cancer
Fact: Skin Cancer Can Develop Without Symptoms
Some types of skin cancer do not cause pain or visible changes at first. A professional skin cancer check is the only way to confirm whether a spot is harmless or requires further investigation.
Myth 8: One Application of Sunscreen Lasts All Day
Fact: Sunscreen Needs Reapplication
Sunscreen wears off due to sweat, water, and normal skin absorption. Reapply sunscreen every two hours, especially when outdoors.
Risk Factors for Skin Cancer
While anyone can develop skin cancer, certain factors increase the risk:
- Excessive sun exposure without protection.
- A history of sunburns, especially blistering sunburns.
- A weakened immune system due to medical conditions or medications.
- Genetic predisposition family history of melanoma.
- Frequent use of tanning beds.
- Fair skin, light hair, and freckles, which increase sensitivity to UV rays.
Reducing exposure to these risks helps lower the chances of developing skin cancer.
Warning Signs of Skin Cancer
Early detection increases survival rates. Look for changes in the skin, including:
- A new mole or an existing one changing in size, shape, or color.
- A sore that does not heal.
- A spot that itches, bleeds, or becomes painful.
- A patch of skin that appears different from surrounding areas.
The ABCDE rule helps identify suspicious moles:
- A – Asymmetry: One half is different from the other.
- B – Border: Edges are irregular or blurred.
- C – Color: Uneven color with multiple shades.
- D – Diameter: Larger than 6mm (pencil eraser size).
- E – Evolving: Changing in size, shape, or texture.
If you notice any of these, visit a skin cancer clinic immediately.
Preventing Skin Cancer
Protecting your skin reduces the risk of skin cancer. Follow these prevention tips:
- Use sunscreen daily with SPF 30+.
- Wear protective clothing, including hats and sunglasses.
- Avoid tanning beds and direct sun exposure between 10 AM and 4 PM.
- Seek shade when outdoors.
- Get regular skin cancer checks at a trusted clinic.
When to See a Skin Cancer Specialist
Visit a skin cancer clinic if you notice:
- A mole or lesion that changes.
- A wound that does not heal.
- A new growth that looks unusual.
- Persistent itching, bleeding, or discomfort on any skin area.
Early detection saves lives. Do not ignore unusual skin changes.
Get a Skin Cancer Check at Paterson Healthcare
At Paterson Healthcare (16 King St, Paterson NSW 2421, Australia), we provide expert skin cancer screenings to detect issues early. Our team offers guidance on prevention, detection, and treatment.
Book an appointment today for a professional skin cancer check.
Call now or visit our clinic for expert care.
By staying informed and proactive, you can reduce the risk of skin cancer and maintain healthy skin. Protect yourself and your loved ones by scheduling a skin check today.